Quiz
capability to list the pods inside the namespace default.
Create a new Pod named backend-pod in the namespace default, mount the newly created sa
backend-sa to the pod, and Verify that the pod is able to list pods.
Ensure that the Pod is running.
A service account provides an identity for processes that run in a Pod.
Quiz
effect.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the API server:-
a. Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes RBAC
b. Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes Node
c. Ensure that the --profiling argument is set to false
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the Kubelet:-
a. Ensure the --anonymous-auth argument is set to false.
b. Ensure that the --authorization-mode argument is set to Webhook.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the ETCD:-
a. Ensure that the --auto-tls argument is not set to true
Hint: Take the use of Tool Kube-Bench
Explanation below.
API server:
Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes RBAC
Turn on Role Based Access Control.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) allows fine-grained control over the operations that different
entities can perform on different objects in the cluster. It is recommended to use the RBAC
authorization mode.
Fix - Buildtime
Kubernetes
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
component: kube-apiserver
tier: control-plane
name: kube-apiserver
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- command:
+ - kube-apiserver
+ - --authorization-mode=RBAC,Node
image: gcr.io/google_containers/kube-apiserver-amd64:v1.6.0
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 8
httpGet:
host: 127.0.0.1
path: /healthz
port: 6443
scheme: HTTPS
initialDelaySeconds: 15
timeoutSeconds: 15
name: kube-apiserver-should-pass
resources:
requests:
cpu: 250m
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/
name: k8s
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs
name: certs
- mountPath: /etc/pki
name: pki
hostNetwork: true
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /etc/kubernetes
name: k8s
- hostPath:
path: /etc/ssl/certs
name: certs
- hostPath:
path: /etc/pki
name: pki
Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes Node
Remediation: Edit the API server pod specification file /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-
apiserver.yaml on the master node and set the --authorization-mode parameter to a value that
includes Node.
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
Audit:
/bin/ps -ef | grep kube-apiserver | grep -v grep
Expected result:
'Node,RBAC' has 'Node'
Ensure that the --profiling argument is set to false
Remediation: Edit the API server pod specification file /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-
apiserver.yaml on the master node and set the below parameter.
--profiling=false
Audit:
/bin/ps -ef | grep kube-apiserver | grep -v grep
Expected result:
'false' is equal to 'false'
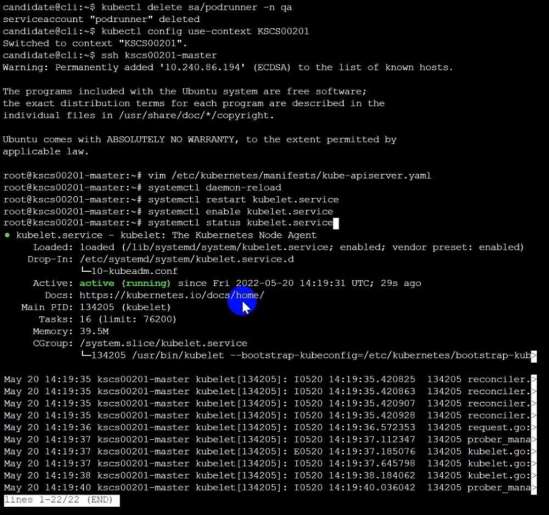
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the Kubelet:-
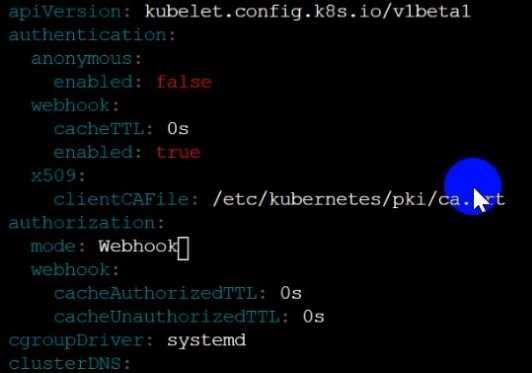
Ensure the --anonymous-auth argument is set to false.
Remediation: If using a Kubelet config file, edit the file to set authentication: anonymous: enabled
to false. If using executable arguments, edit the kubelet service
file /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf on each worker node and set the
below parameter in KUBELET_SYSTEM_PODS_ARGS variable.
--anonymous-auth=false
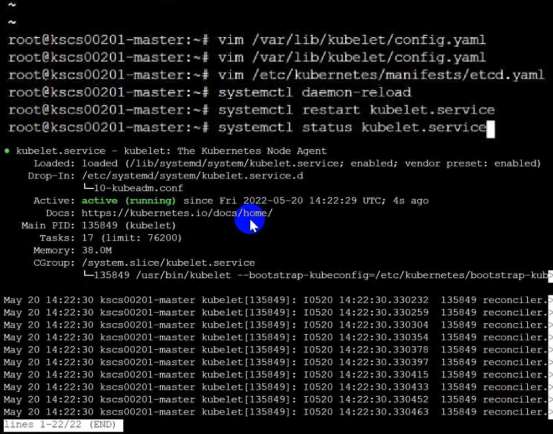
Based on your system, restart the kubelet service. For example:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart kubelet.service
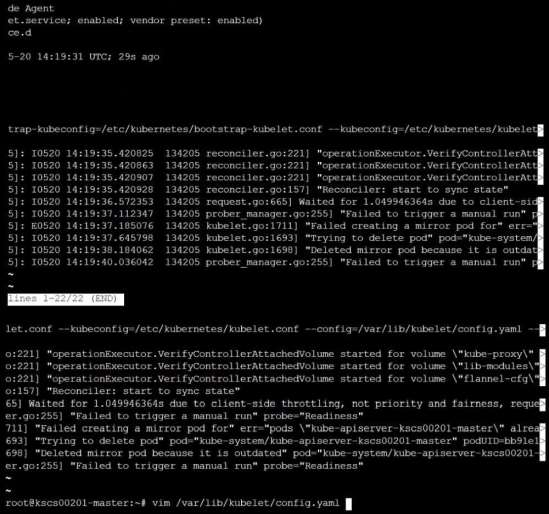
Audit:
/bin/ps -fC kubelet
Audit Config:
/bin/cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
Expected result:
'false' is equal to 'false'
2) Ensure that the --authorization-mode argument is set to Webhook.
Audit
docker inspect kubelet | jq -e '.[0].Args[] | match("--authorization-mode=Webhook").string'
Returned Value: --authorization-mode=Webhook
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the ETCD:-
a. Ensure that the --auto-tls argument is not set to true
Do not use self-signed certificates for TLS. etcd is a highly-available key value store used by
Kubernetes deployments for persistent storage of all of its REST API objects. These objects are
sensitive in nature and should not be available to unauthenticated clients. You should enable the
client authentication via valid certificates to secure the access to the etcd service.
Fix - Buildtime
Kubernetes
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
scheduler.alpha.kubernetes.io/critical-pod: ""
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
component: etcd
tier: control-plane
name: etcd
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- command:
+ - etcd
+ - --auto-tls=true
image: k8s.gcr.io/etcd-amd64:3.2.18
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/sh
- -ec
- ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --endpoints=https://[192.168.22.9]:2379 --
cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/healthcheck-client.crt --
key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/healthcheck-client.key
get foo
failureThreshold: 8
initialDelaySeconds: 15
timeoutSeconds: 15
name: etcd-should-fail
resources: {}
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/etcd
name: etcd-data
- mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
name: etcd-certs
hostNetwork: true
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /var/lib/etcd
type: DirectoryOrCreate
name: etcd-data
- hostPath:
path: /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
type: DirectoryOrCreate
name: etcd-certs
status: {}
Quiz
Create a new PodSecurityPolicy named prevent-privileged-policy which prevents the creation of
privileged pods.
Create a new ServiceAccount named psp-sa in the namespace default.
Create a new ClusterRole named prevent-role, which uses the newly created Pod Security Policy
prevent-privileged-policy.
Create a new ClusterRoleBinding named prevent-role-binding, which binds the created ClusterRole
prevent-role to the created SA psp-sa.
Also, Check the Configuration is working or not by trying to Create a Privileged pod, it should get
failed.
Quiz

Context
A Role bound to a Pod's ServiceAccount grants overly permissive permissions. Complete the
following tasks to reduce the set of permissions.
Task
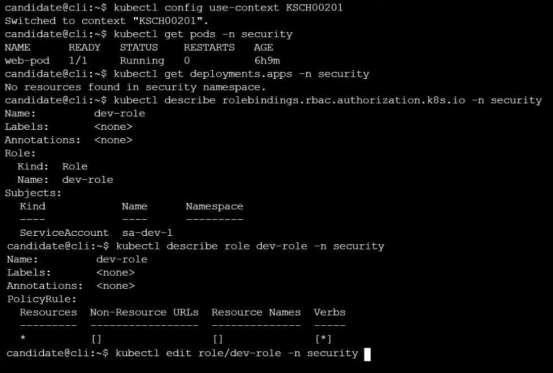
Given an existing Pod named web-pod running in the namespace security.
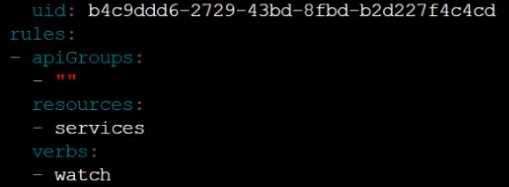
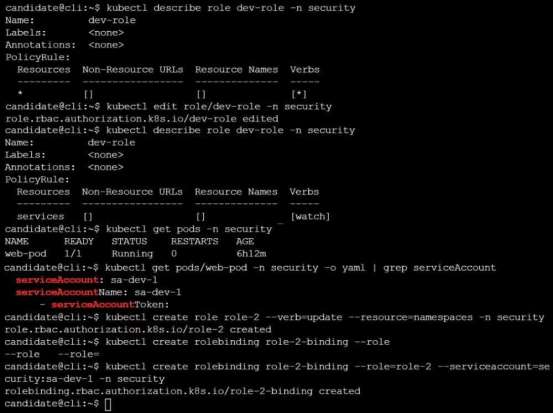
Edit the existing Role bound to the Pod's ServiceAccount sa-dev-1 to only allow performing watch
operations, only on resources of type services.
Create a new Role named role-2 in the namespace security, which only allows performing update
operations, only on resources of type namespaces.
Create a new RoleBinding named role-2-binding binding the newly created Role to the Pod's
ServiceAccount.

explanation below.
Quiz
1. logs are stored at /var/log/kubernetes-logs.txt.
2. Log files are retained for 12 days.
3. at maximum, a number of 8 old audit logs files are retained.
4. set the maximum size before getting rotated to 200MB
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. namespaces changes at RequestResponse
2. Log the request body of secrets changes in the namespace kube-system.
3. Log all other resources in core and extensions at the Request level.
4. Log "pods/portforward", "services/proxy" at Metadata level.
5. Omit the Stage RequestReceived
All other requests at the Metadata level
Quiz
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update -y
RUN apt-install nginx -y
COPY entrypoint.sh /
ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"]
USER ROOT
Fixing two instructions present in the file being prominent security best practice issues
Analyze and edit the deployment manifest file
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: security-context-demo-2
spec:
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
containers:
- name: sec-ctx-demo-2
image: gcr.io/google-samples/node-hello:1.0
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
privileged: True
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
Fixing two fields present in the file being prominent security best practice issues
Don't add or remove configuration settings; only modify the existing configuration settings
Whenever you need an unprivileged user for any of the tasks, use user test-user with the user id
5487
Quiz
Create a Pods of image Nginx in the Namespace server to run on the gVisor runtime class
Install the Runtime Class for gVisor
{ # Step 1: Install a RuntimeClass
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RuntimeClass
metadata:
name: gvisor
handler: runsc
EOF
}
Create a Pod with the gVisor Runtime Class
{ # Step 2: Create a pod
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-gvisor
spec:
runtimeClassName: gvisor
Quiz

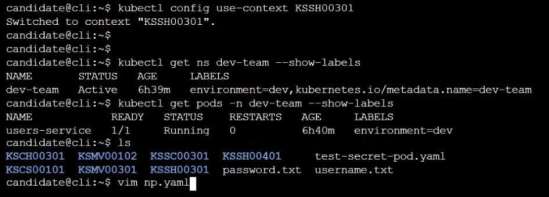
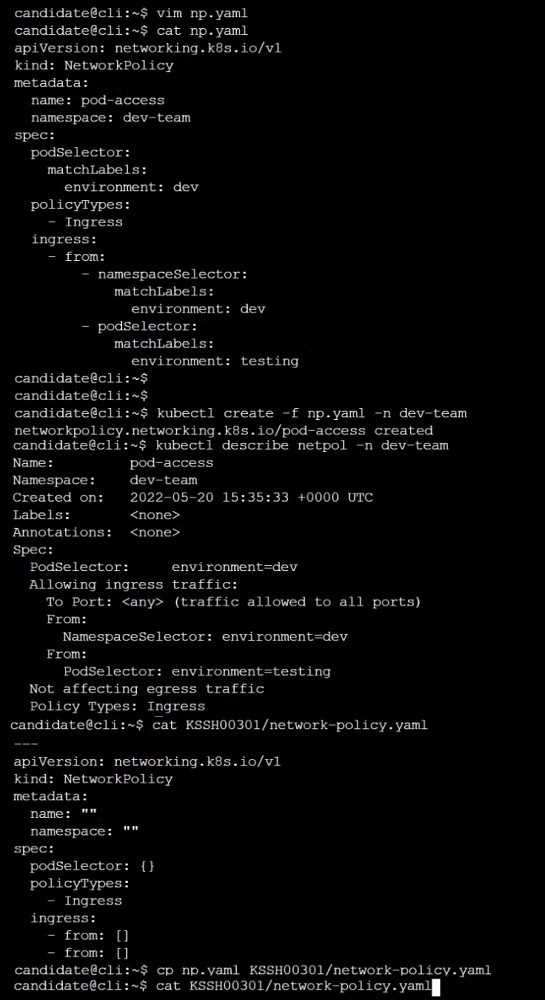
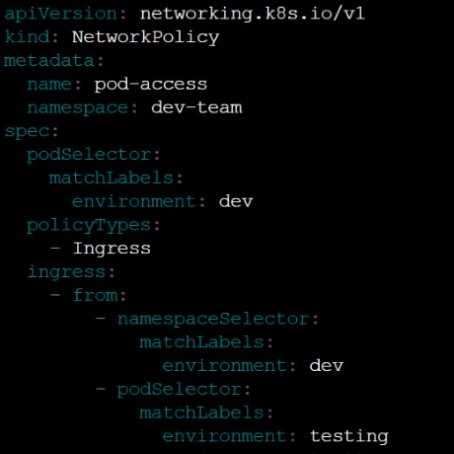
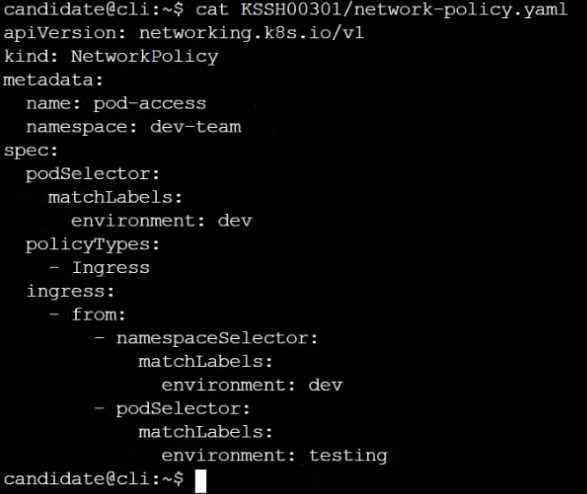
Task
Create a NetworkPolicy named pod-access to restrict access to Pod users-service running in
namespace dev-team.
Only allow the following Pods to connect to Pod users-service:
Pods in the namespace qa

Pods with label environment: testing, in any namespace

explanation below.
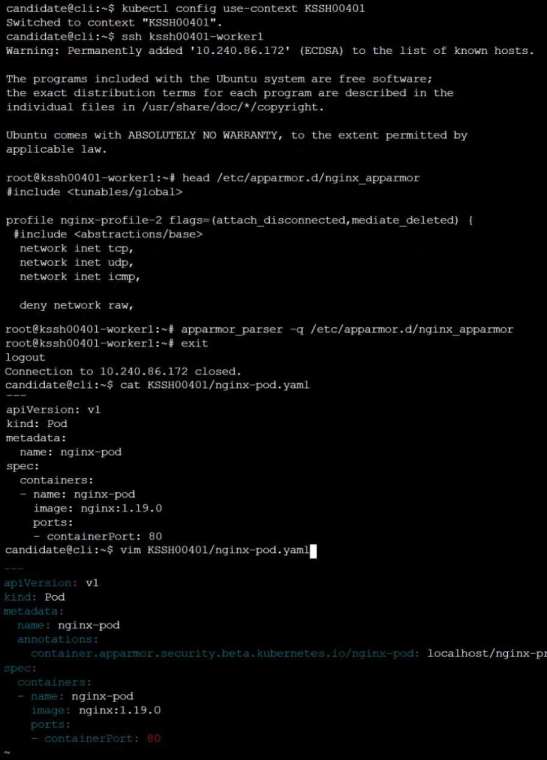
Quiz
#include <tunables/global>
profile nginx-deny flags=(attach_disconnected) {
#include <abstractions/base>
file,
# Deny all file writes.
deny /** w,
}
EOF'
Edit the prepared manifest file to include the AppArmor profile.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: apparmor-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: apparmor-pod
image: nginx
Finally, apply the manifests files and create the Pod specified on it.
Verify: Try to make a file inside the directory which is restricted.
explanation below.

Quiz
ingress and egress traffic
Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Practice test unlocks all online simulator questions
Thank you for choosing the free version of the Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist practice test! Further deepen your knowledge on Linux Foundation Simulator; by unlocking the full version of our Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator you will be able to take tests with over 45 constantly updated questions and easily pass your exam. 98% of people pass the exam in the first attempt after preparing with our 45 questions.
BUY NOWWhat to expect from our Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist practice tests and how to prepare for any exam?
The Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator Practice Tests are part of the Linux Foundation Database and are the best way to prepare for any Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist exam. The Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist practice tests consist of 45 questions and are written by experts to help you and prepare you to pass the exam on the first attempt. The Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist database includes questions from previous and other exams, which means you will be able to practice simulating past and future questions. Preparation with Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator will also give you an idea of the time it will take to complete each section of the Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist practice test . It is important to note that the Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator does not replace the classic Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist study guides; however, the Simulator provides valuable insights into what to expect and how much work needs to be done to prepare for the Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist exam.
BUY NOWLinux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Practice test therefore represents an excellent tool to prepare for the actual exam together with our Linux Foundation practice test . Our Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator will help you assess your level of preparation and understand your strengths and weaknesses. Below you can read all the quizzes you will find in our Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator and how our unique Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Database made up of real questions:
Info quiz:
- Quiz name:Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist
- Total number of questions:45
- Number of questions for the test:50
- Pass score:80%
You can prepare for the Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist exams with our mobile app. It is very easy to use and even works offline in case of network failure, with all the functions you need to study and practice with our Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator.
Use our Mobile App, available for both Android and iOS devices, with our Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Simulator . You can use it anywhere and always remember that our mobile app is free and available on all stores.
Our Mobile App contains all Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist practice tests which consist of 45 questions and also provide study material to pass the final Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist exam with guaranteed success. Our Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist database contain hundreds of questions and Linux Foundation Tests related to Linux Foundation Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Exam. This way you can practice anywhere you want, even offline without the internet.
BUY NOW